Thyroid Nodules: Symptoms And Causes
Thyroid nodules are the result of cell growth that takes the form of bumps or bulges. Some can be felt with simple palpation, but most are small and escape physical examination.
Nodules can be solid or cystic. The former contain liquid inside, wrapped in a capsule: the solid ones, on the other hand, are hard in their entire structure. They can form in different places in the thyroid gland; this consists of two lobes joined by a central segment. The thyroid is located in the neck and under normal conditions it is not possible to feel it by palpation.
One of the functions of the thyroid is to produce the hormones T3 and T4; it could therefore happen that even a thyroid nodule is functional, that is, able to secrete hormones like the rest of the gland. In this case, symptoms related to excessive hormone production will be present.
Thyroid nodules are mostly benign and are often spotted accidentally, such as during a medical check-up for other reasons. Although only a small percentage of thyroid nodules correspond to a cancerous form, it is necessary to undergo all the necessary tests for diagnosis.
Causes of thyroid nodules
The causes that lead to the appearance of a thyroid nodule are diverse, from a change in diet to the growth of malignant cells. Let’s see some of the most important.
Dietary iodine deficiency
When iodine is not present in sufficient quantities in the diet, the thyroid can react by producing nodules. This is a classic and historical reason for thyroid malfunction. In many countries, health has taken measures in this regard, making it mandatory to add iodine to some foods, starting with table salt.
This law was enacted at a time when there was a high incidence of goiter, an enlarged thyroid gland caused by a lack of iodine, in many states around the world.
Thyroiditis
When the inflammation of the thyroid gland becomes chronic, it can generate nodules. One of the best known varieties of this disease is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, with the symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Multiplication of normal thyroid cells
In some circumstances, normal thyroid cells overgrow, creating a lump. This phenomenon is known as thyroid adenoma and is benign.
However, the adenoma may also be functional, i.e. capable of producing hormones and pouring them into the blood. This can lead to hyperthyroidism.
Accumulation of liquid
Thyroid nodules can be cystic – fluid-filled cavities. They are benign and usually non-functional (unable to secrete hormones).
Proliferation of malignant cells
The most dangerous form of thyroid nodules is thyroid cancer. Fortunately, it accounts for a very small percentage of cases. With an early diagnosis it is possible to keep it under control by drug therapy or surgery.
Symptoms of thyroid nodules
Nodules are usually asymptomatic as they tend to be small and non-functional. In many cases they are discovered during an ultrasound or a tomography of the neck dictated by other reasons.
When the lump is detectable from the outside by palpation of the neck, it is in the presence of a rather large formation. These abnormalities can be detected by the physician while performing a physical exam or by the patient himself.
If other symptoms such as weight loss, heavy sweating, heart rhythm changes, or difficulty swallowing are present with the lump, malignancy of the lump may be suspected. Although the diagnosis is often favorable, the presence of these symptoms requires rapidity in the implementation of complementary diagnostic methods.
On the other hand, if the thyroid nodules are functional and capable of secreting hormones, the symptoms are those of hyperthyroidism. This will result in tachycardia, fatigue, changes in nails and hair, irritability and inability to gain weight despite a more abundant diet.
Diagnosis of thyroid nodules
After detecting a lump by palpation or an examination performed for other reasons, the doctor prescribes a series of tests. Among the diagnostic tests that help to specify the type of injury we find:
- Dosage of thyroid hormones ; through blood tests the levels of T4 and TSH are measured.
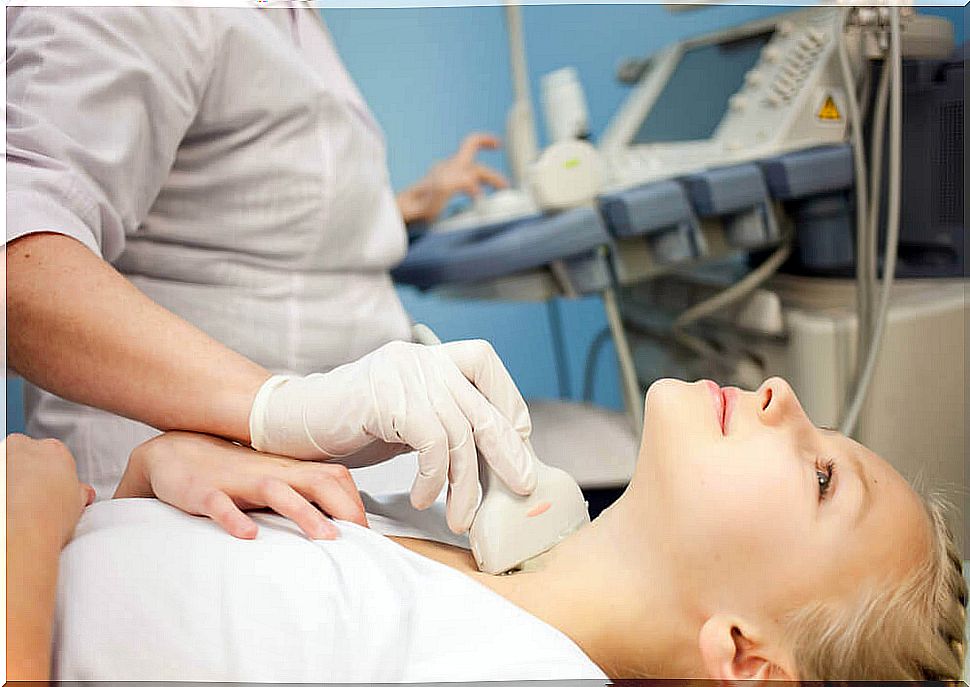
- Thyroid ultrasound : if not previously requested, this is the first step to take. Ultrasound allows, in the first place, to distinguish between solid and cystic nodules, as well as to define their size.
- Needle aspiration biopsy : Required especially when a malignant nodule is suspected. A very fine needle is introduced into the gland to extract some cells to be analyzed under a microscope. It is performed on an outpatient basis, without the need for hospitalization, usually with local anesthesia alone.
In short
Thyroid nodules are the result of various types of thyroid abnormalities. Although they are generally benign, an adequate diagnosis is always necessary to rule out more serious problems. Any of the above symptoms should be reported to the doctor immediately.