Symptoms Of Hypoglycemia: What Are They?

When there is a slight drop in blood sugar levels, the symptoms of hypoglycemia can be confused with other clinical pictures. It may even happen that with the intake of a food rich in carbohydrates they go unnoticed.
We speak of hypoglycemia when the value of blood sugar, or sugar in the blood, is lowered. To be exact, hypoglycemia is diagnosed when the amount of glucose in the blood is less than 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg / dL).
The causes are different and we will see them shortly, but first of all it is interesting to understand how our body absorbs glucose. The processing mechanism contains the answer that explains how, in the event of an error, the symptoms of hypoglycemia occur.
The human being absorbs glucose from food, which does not necessarily have to be sugary or sweet. The body will also extract glucose molecules from fruits and vegetables. To be functional, glucose must penetrate tissue cells. Here it will be transformed into energy fuel for the functions of each cell. This mechanism of entry into cells is regulated by insulin.
The role of insulin
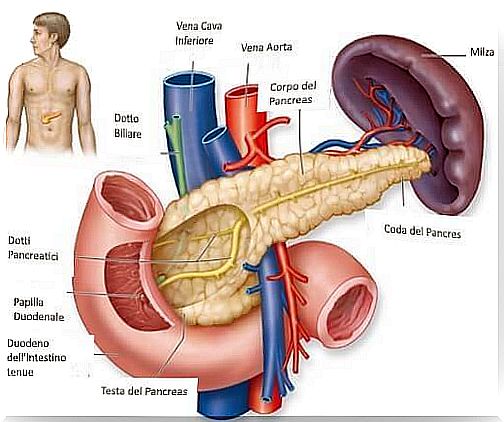
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas, which regulates excess sugar in the blood. It is the missing hormone in individuals with diabetes.
The antagonist of insulin is glucagon, another hormone secreted by the pancreas. Glucagon has the task of stimulating the liver to break down stored glycogen and circulate glucose in the blood. Broadly speaking, we could say that insulin lowers blood sugar and glucagon raises it.
It is this hormonal play, together with other factors, that can give rise to the symptoms of hypoglycemia. It will be mild or severe based on the amount of glucose in the bloodstream.
Symptoms of mild hypoglycemia
Symptoms of mild hypoglycemia very often go unnoticed. That is, there is a lowering of blood sugar levels that is not significant to the point of having a serious impact on vital organs. Among the symptoms we have:
- Profuse sweating.
- Headache or headache.
- Vertigo, lack of motor coordination and impaired vision.
- Drowsiness. Sometimes, more than actual sleep, it is a question of difficulty concentrating, as if the mind were muffled.
- Muscle tremors.

Symptoms of severe hypoglycemia
In extreme cases, when hypoglycemia is significant and blood sugar levels drop sharply, the symptoms are:
- Seizures : Usually, in the form of intense muscle movements, such as jolts.
- Fainting with loss of consciousness: This can last a long time and the person may not recover right away.
- Inability to eat : sometimes it is an isolated symptom of hypoglycemia, while others are part of a picture of convulsions and fainting.
Causes of hypoglycemia
There are five causes behind the symptoms of hypoglycemia. In principle, there are predictable causes, except for insulinoma, although the latter is rare:
- Diabetes: paradoxically, even if it is a disease that increases blood sugar levels, it represents the most frequent cause of hypoglycemia. This aspect is caused by the drugs used in the treatment of diabetes. At the beginning of therapy, until the right dose is found or due to the habits of the diabetic person, the blood sugar can drop sharply.
- Alcohol : Symptoms of hypoglycemia are not uncommon in people with alcoholism, because alcohol stops the liver from secreting glucose. This aspect usually adds up to the long periods of fasting that an alcoholic faces, not eating enough or following the meals of the day.
- Prolonged fasting : By spending long periods of fasting, however much glucagon is initially activated, there will come a time when it will not be enough. Diseases such as anorexia nervosa cause prolonged fasting. Without nutrition, there is no glucose supply to the body.
- Pharmacological therapy : in addition to the drugs taken in case of diabetes, other drugs also have hypoglycemia among their side effects. We can mention quinine, for the treatment of malaria, or gatifloxacin (an antibiotic).
- Insulinoma: There is a pancreatic cancer that occurs due to the overgrowth of the cells that produce insulin. Obviously, due to the increased amount of insulin in the body, hypoglycemic episodes occur.
What to do in case of hypoglycemia
As we have just seen, the symptoms of hypoglycemia can be mild or severe. Based on this ranking, the intervention plan will vary, case by case.
If the hypoglycemia is mild, the most effective measure is the administration of fluids that offer the patient a rapid availability of glucose. Among these preparations we have a glass of water with two tablespoons of sugar, a sip of a sweetened drink such as carbonated ones or about 200 ml of fruit juice, for example.
On the other hand, in cases of severe hypoglycemia, food cannot be given to the patient, as he will be unconscious or convulsed. In these cases, doctors administer the hormone glucagon in an injectable artificial form.