Levodopa, A Drug For Parkinson’s Patients
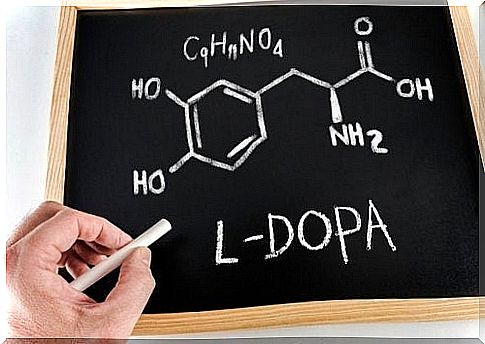
Levodopa is the basic therapy of Parkinson’s disease. It is given to treat this disease, in combination with other dopa decarboxylase inhibitor drugs, such as carbidopa or benserazide .
It is a medicine belonging to the therapeutic family of antiparkinsonians. Levodopa is a drug that acts on the central nervous system , turning into dopamine when it reaches the brain.
A brief history of Parkinson’s disease
The first person to associate Parkinson’s disease with a dopamine deficiency was biochemist Oleh Hornykiewicz. He examined the autopsies of patients suffering from Parkinson’s disease and suggested such a relationship. Later, this scientist began treating patients with a racemic mixture of DOPA, with positive results.
Not long after, another scientist, Curt Porter, showed that the L-DOPA stereoisomer was the really active one , reducing the effective dose of the compound in half. Subsequently, they started synthesizing different molecules, such as benzeraside or carbidopa , improving the results in the treatment. With the latter drugs they also managed to reduce the dose needed to achieve the desired effects.
Know some aspects of Parkinson’s disease

Parkinson’s disease is a central nervous system disease caused by a deficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine in striated neurons which, in turn, results from the death of nigrostriatal neurons.
The origin of this disease is multifactorial and has a high incidence in the general population, particularly among the elderly. To be exact, it affects 2% of people over 65. However, it can also occur in young people.
Parkinson’s presents a very peculiar symptom, and for which it is often defined, which consists in the appearance of tremors . This symptom affects over 60% of patients. However, other motor symptoms may also occur such as:
- Rigidity.
- Slow movements , also known as bradykinesia.
- Alterations in reflexes and postural falls.
Other symptoms that can occur with the course of the disease are:
- Dementia and memory loss .
- Hallucinations.
- Depression.
- Dysphagia.
- Muscular pain.
- Neuropathic pain.
On the other hand, this disease is known to be related to an increase in α-synuclein protein , also related to Alzheimer’s. The therapeutic strategy is therefore based on the administration of alpha-synuclein aggregation inhibitors or immunization for these protein derivatives. A study conducted with nilotinib seeks to investigate this therapy.
The general characteristics of Levodopa therapy
Levodopa therapy for Parkinson’s consists of trying to increase dopamine levels by acting directly on the receptors. This occurs by inhibiting the breakdown of the neurotransmitter or LAAD, the enzyme that transforms dopa into dopamine.
In this sense, one might wonder why dopamine is not administered directly to the patient. The problem is that it has a high rate of recapture and metabolization, which prevents its absorption. Furthermore, dopamine is a very water-soluble molecule and, therefore, is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier that protects the brain.
For all these reasons, Parkinson’s disease is treated with the dopamine precursor , levodopa . This substance manages to cross the blood-brain barrier and turns into dopamine when it reaches the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Although levodopa crosses the blood-brain barrier very well, it has a strong peripheral metabolism, so the amount that reaches the brain is very small.
To solve this problem, it is administered together with other drugs that inhibit the LAAD enzyme , as we have already mentioned. In this way, it is possible to inhibit the transformation of levodopa into dopamine at the peripheral level and, ultimately, it reaches the brain in greater quantities.
Advantages of administering levodopa together with LAAD inhibitors

Co-administration of these drugs reduces the amount of levodopa to be administered by 75%, as they increase its half-life and help maintain more stable levels in the brain .
Its administration therefore obtains greater clinical efficacy, which manifests itself in a faster action. By reducing the amount of dopamine in peripheral tissues, cardiovascular and gastrointestinal effects decrease . Consequently, levodopa is always given together with benzeraside or carbidopa.
Conclusion
Levodopa is the first line of treatment to combat Parkinson’s disease . It is given together with other drugs to increase their effectiveness.
You can consult your doctor or pharmacist with any questions about this disease and its treatment, as well as to inquire about progress and clinical trials currently underway.