Intubation Drugs: What Are They?
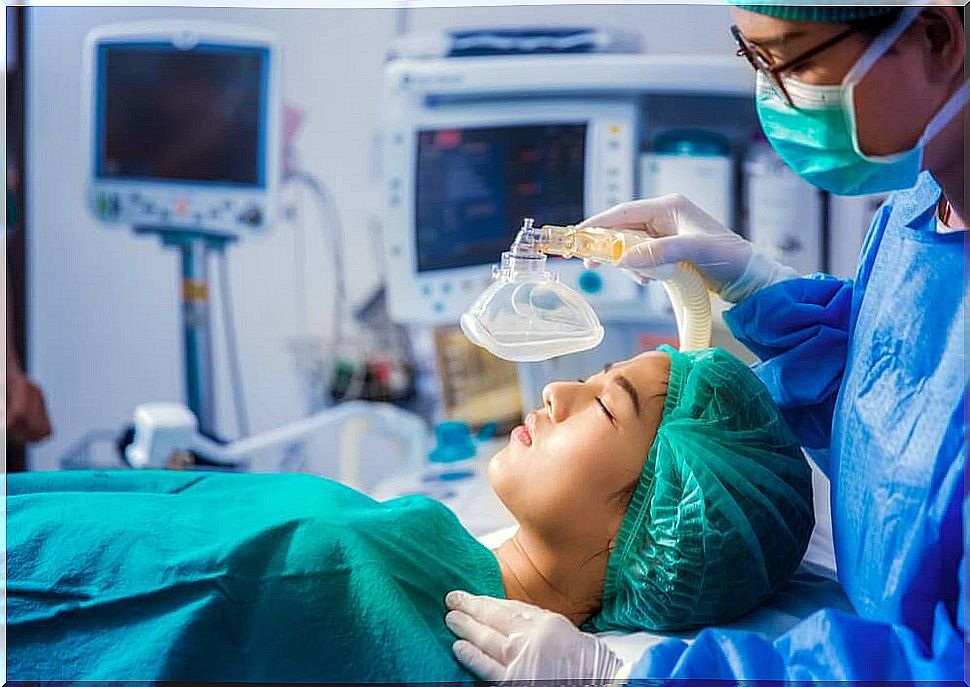
Airway obstruction and hyperventilation are two of the causes of death and / or severe morbidity in adults and the elderly. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation techniques, such as intubation, are among the most important in the management of this type of emergency. Today we will see what intubation drugs are.
Intubation is a very common procedure in the emergency room and in intensive care, and this regardless of the pathology for which it is necessary to manipulate the airways.
This procedure presents difficulties due to the anatomy of the larynx structure, the limited time available to intervene on the problem and poor visibility. Precisely for this reason , specific drugs are administered that can facilitate the intubation procedure by the doctor.
What does an intubation consist of?
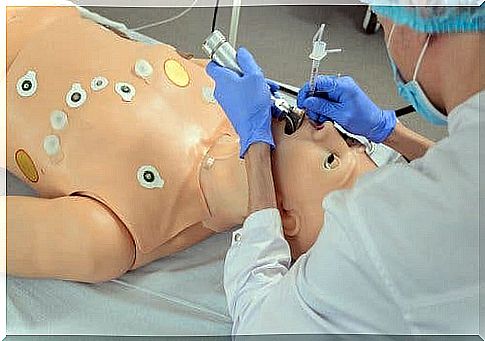
Intubation consists of the rapid introduction of a tube along the trachea in order to create a conduit for the passage of air. When the tube is inserted, the patient can more easily manage the functioning of the airway.
Intubation is the technique of choice when it comes to taking control of a patient’s airways, precisely because of the advantages it offers. On the one hand, it isolates the airways, allowing the permeability to be maintained. In addition, it prevents gastric insufflation, which means it prevents the stomach from filling with air.
On the other hand, it stimulates deep tracheal aspiration, as well as ensuring the administration of a high concentration of oxygen. This procedure also eliminates the need to seal mask-to-face contact and represents an additional route of drug delivery.
In which cases is this technique used?
There are precise indications on when to perform this procedure, and the most common is cardiorespiratory arrest. Yet, there are many other situations that require intubation.
Patients with a need for isolation or protection of the respiratory tract, those who have suffered a head injury with Glasgow scale of less than 8 points or those who suffer from respiratory insufficiency above 30 or below 10 breaths per minute will be undergoing intubation.
Intubation can also be performed in those who have suffered from a respiratory crisis or in those with airway edema due to burns or anaphylaxis.
Intubation drugs
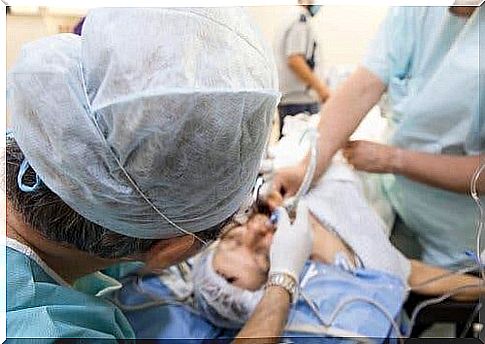
During intubation the body produces a powerful adrenergic discharge response, accompanied by tachycardia, hypertension and increased intracranial and ocular pressure.
For this purpose, a phase has been described which takes the name of pre-oxygenation and during which the following drugs are administered in order to limit the physiological response:
- Lidocaine: indicated in patients with intracranial hypertension or with increased bronchial reactivity. The recommended dose of lidocaine is 1.5 mg / kg of weight, preferably 3 minutes before intubation.
- Fentanyl: is an opioid that reduces the sympathetic response, i.e. tachycardia and arterial hypotension. Care should be taken in administering this drug, as it is responsible for respiratory depression.
- Atropine: Recommended in the prevention of bradycardia in pediatric patients.
- Dosage of neuromuscular blocker for defasciculating purposes. This method is not currently recommended, as the real benefits of reduced collation are not known. However, we know the side effects of these medicines.
Other intubation drugs
As for the induction and paralysis phase, sedative drugs are administered in sequence that induce unconsciousness and, therefore, a muscle relaxant, generally succinylcholine. Among the neuromuscular blockers and inducing agents most used in clinical practice stand out:
- Etomidato : is the most widely used inducer with a hypnotic effect. It does not affect hemodynamics.
- Ketamine: it is the only drug that for hemodynamic stability can be compared to etomidate. It is a dissociative anesthetic. It stimulates the release of catecholamines, which results in an increase in heart rate, blood pressure and cardiac output. Most suitable for hypothesis patients.
- Propofol: is a drug widely used in anesthetic induction as it is a sedative-hypnotic with an ultra-fast action. It initially acts with a rapid action and has a short duration, in addition it has antiemetic actions.
- Barbiturates: Thiopental is widely used in anesthesia, as is propofol. It is recommended for patients with suspected haemodynamically unstable intracranial hypertension.
- Benzodiazepines: midazolam is the most widely used drug in its category due to its relatively rapid effect and short duration compared to that of other drugs of the same family. On top of that, it has a more powerful amnesic effect.