Burning Mouth Syndrome: Symptoms And Causes
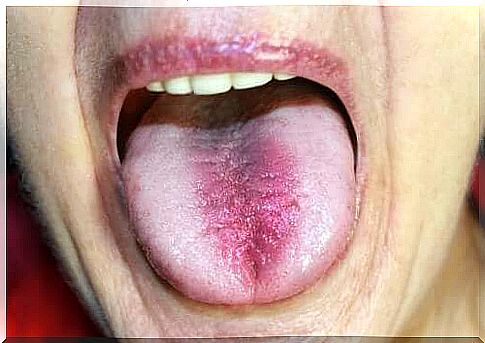
Burning mouth syndrome, also known as glossodynia, is a condition characterized by xerostomia in women aged 50 and over.
Saliva is a fundamental element for the health of the oral cavity, as it acts as a natural lubricant of the tissues of the mouth. It is also essential for digestion, as it contributes to the formation of the food bolus. Finally, it prevents the development of ailments such as tooth decay or periodontal diseases.
What is xerostomia?
It is the reduction of salivary flow at rest and has a high incidence from the age of fifty, especially in women, because they are subject to hormonal imbalances.
It can be a transient pathology, for example associated with a state of anxiety, infection and other factors. But it can also be chronic if associated with the consumption of alcohol, tobacco, chemotherapy, etc.
What is burning mouth syndrome?
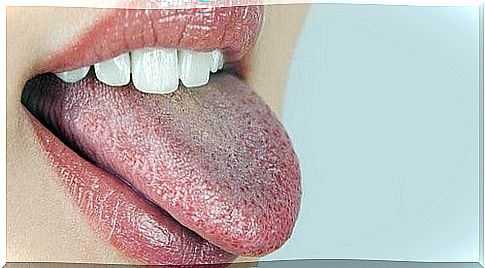
As anticipated, it is a pathology characterized by xerostomia, especially in women aged fifty and over. It is associated with hormonal imbalances, such as menopause. Typically, it is three times more common in women than in men.
Symptoms of burning mouth syndrome
People affected by this syndrome also manifest dysgeusia, or difficulty in swallowing. Hyposalivation is also associated with gingivitis, tooth decay or halitosis. Saliva tends to become more abundant and thick. In addition, the mucosa appears dry, irritated and red. Often the patient also accuses symptoms such as:
- Burning in the mouth and tongue
- Dry lips
- Dry maw
- Presence of ulcers
- Constant thirst
- Increased dental plaque residues
Symptoms typically worsen in the afternoon and evening. Patients also report a metallic or bitter taste. Caries often appear around the collar of the teeth, at the root, precisely because of the reduction in the self-cleaning capacity promoted by saliva.
How can it be treated?
If the cause is peripheral (that is, if it is associated with drugs or other conditions), the syndrome will disappear when these causes resolve. In the event that the syndrome is not caused by external factors, treatment will aim to increase salivation to prevent the side effects of hyposalivation.
Medical and nutritional advice should be followed to stimulate increased saliva production. For this purpose, salivary stimulants are often prescribed in combination with salivary substitutes. Typically, they are available in spray form, in the form of toothpaste or mouthwash.
How to prevent this ailment?

To prevent this pathology or to intervene on symptoms in a natural way, we can take into account the following recommendations:
- Try living a more relaxed life by reducing your stress levels.
- Increase your fluid intake, making sure you drink about two liters of water a day.
- Try different mild toothpastes, without an excessive menthol flavor.
- Avoid ingesting acidic liquids and foods, carbonated drinks or coffee.
- Avoid cinnamon.
- Limit your consumption or eliminate alcoholic beverages from your diet, as well as products that contain alcohol.
- Eliminate spicy from the diet.
- Stop smoking tobacco or limit it as much as possible.
To sum up
If we notice changes in the amount of saliva for some time, irritation of the mucous membrane or any other symptoms, we should contact a doctor.
Not only to treat it, but also to rule out other possible pathologies, such as diabetes mellitus or cancer. The doctor or dentist will be the most suitable professionals to identify the possible causes of the disease and formulate the diagnosis.