Atrial Flutter: Symptoms And Causes
Atrial flutter is an arrhythmia, which is a heart rhythm disorder. It consists in the production of rapid and anomalous electrical discharges in the atrium.
Such discharges cause a high contraction of the atria, so only some of these electrical impulses reach the ventricles. This leads them to contract irregularly, faster and less efficiently than normal.
The Atrial flutter is similar to atrial fibrillation. However, in the former the rhythm is more organized than in the fibrillation. It is a relatively frequent ailment. The highest incidence is among 60-year-old men.
In this article, we explain what atrial flutter is and what the symptoms and causes are.
How does atrial flutter occur?
Under normal conditions, the heart cavities (atria and ventricles) contract rhythmically and in synchrony through an electrical impulse . This impulse is generated in the atrium and passes to the ventricle. Following this, the heartbeat occurs.
The normal rate is between 50 and 100 beats per minute. However, in the case of arrhythmia, this mechanism is altered. The heart therefore stops contracting regularly. When the rhythm is greater than 100 beats per minute, it is called a tachyarrhythmia.
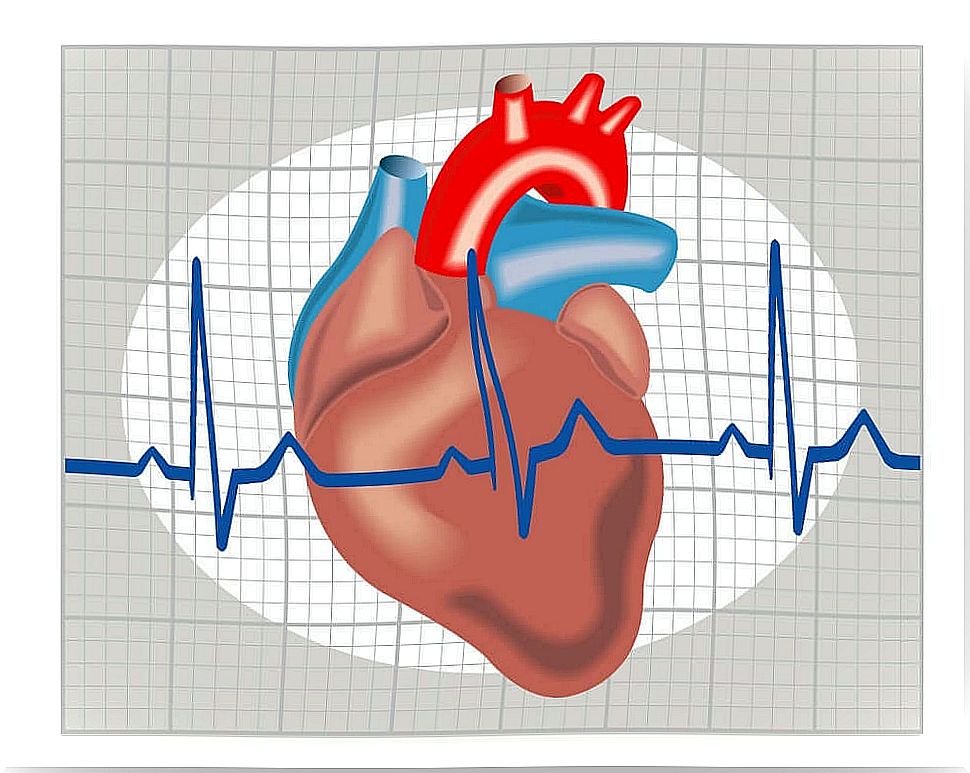
In the case of atrial flutter, the activity of the atria is coordinated. The problem is that they contract at a rate greater than 250 times per minute. As a result, the impulses fail to reach the ventricles properly.
On average, one out of two pulses reaches the ventricles. This results in a heart rate of around 150 beats per minute. In medical terms, atrial flutter is said to be a tachyarrhythmia produced by a macro-orientation circuit.
What are the causes of atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter is a frequent arrhythmia in patients with heart problems. For example, it is more common in people with hypertension, ischemic heart disease or cardiomyopathy. However, it can also occur in people with a healthy heart.
Some of the causes that cause this disorder are:
- Pre-existing cardiac pathologies, as already mentioned. They include heart valve disease and coronary artery disease. Similarly, cardiomyopathies, which are alterations of the heart muscle, also affect.
- Hypertension.
- Consumption of alcohol. A correlation was found with excessive consumption in the short term.
- Other conditions such as lung disorders or hyperthyroidism.
- Previous myocardial infarction. It can also occur in people undergoing coronary revascularization.
- Certain drugs
- Pericarditis.
Symptoms of atrial flutter
Symptoms depend on how fast the ventricles contract. This speed decreases the heart’s ability to pump blood. Symptoms can appear or stop suddenly.
The most frequent symptoms are dizziness and difficulty in breathing. Among others we find:
- Weakness.
- Chest pain, especially in people with other heart problems.
- Pulse accelerated, throbbing and irregular.
- Palpitations.
- Confusion, fainting.
- Loss of strength.
This condition can also be accompanied by complications such as blood clots in the atria. This can happen because, beating too fast, the atria do not empty completely and stagnant blood ends up forming clots.
Fragments of the clot can break off and move through the bloodstream. If they clog an artery, they can cause ischemic problems in other areas of the body. For example, pulmonary thromboembolism or stroke.
Diagnosis
First, the doctor will ausculate the heart and measure the heart rate. Diagnosis is usually based on frequency, symptoms, and an electrocardiogram.
However, atrial flutter can also be intermittent. For this purpose, there are methods that record heart rates over a longer period of time. Among them we find:
- Event monitor, prolonged monitoring (3-4 weeks)
- Holter (24-hour exam)
- Implantable subcutaneous recorder (extended monitoring)
Also, as mentioned, atrial flutter often occurs in patients with persistent heart disease. Therefore, tests such as echocardiography and angiography are also usually done. Blood tests are also done to evaluate thyroid activity.
In conclusion
Atrial flutter is a relatively common heart rhythm disorder. It is therefore important to learn to recognize the symptoms and consult the doctor when faced with the first signs. In this way it will be possible to avoid complications and further heart problems.