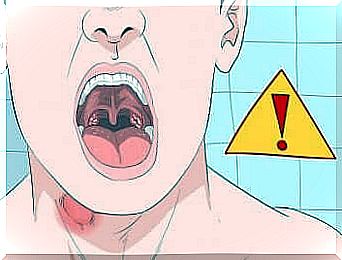
Aphthous Stomatitis: Causes And Treatments

We speak of aphthous stomatitis when small lesions (canker sores) appear in the oral cavity. It is associated with a weakened immune system.
Do you want to know the causes and possible treatments? In the following lines you will find some information about aphthous stomatitis offered by specialists Ramón Bonet and Antonieta Garrote.
What does aphthous stomatitis consist of
This or disorder usually begins in adolescence, although it sometimes begins later in life. Only one or several lesions may appear.
Aphthae have a yellowish white color and red edges; they tend to disappear within a week. Often, however, they cause burning and pain, and sometimes swelling.

Aphthous stomatitis is a benign condition that can become chronic and present several times within a year; in some cases, serious complications arise.
In the most extreme cases, it even causes serious weight loss because the person experiences unbearable pain when trying to eat.
Causes of aphthous stomatitis
The exact cause of this disorder is unknown, but we know that it is associated with a decline in the immune system. The following triggers are also suspected:
- A certain family predisposition has been demonstrated. It often happens that several members of the same family suffer from aphthous stomatitis.
- Stress is present in numerous episodes. Although there is no scientific evidence, it is believed that stress weakens the immune system predisposing the subject to the appearance of mouth ulcers.

- The trauma affecting the oral mucosa as a result of accidental bites.
- In some patients, low levels of iron, folic acid, or vitamin B12 have been found.
- Aphthous stomatitis has also been associated with the consumption of acidic foods and the presence of gastroesophageal reflux.
- The role of some food allergies is suspected, especially to sodium lauryl sulfate used in toothpastes.
Curious data on the medical course
Despite the suspected triggers listed, in most cases aphthous stomatitis is an idiopathic disease, i.e. of unknown origin. However, we have some data on this:
- It is not an infectious disease.
- It is excluded that it is produced by the herpes virus.
- It is not contagious.
Mouth ulcers disappear when the cause is identified and treated. If this fails, experts resort to symptomatic and supportive treatments in order to soothe the pain or burning.
When hygiene measures prove insufficient, pharmacological treatments are used. It is important to emphasize that sometimes it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis to exclude the presence of pathologies that cause oral ulcers. Among the various tests, it is also possible to resort to biopsy.
It is therefore important to seek medical advice and avoid self-medication, since inadequate intervention could mask the symptoms and worsen the prognosis.
Preventive measures
- Use a toothbrush with soft bristles.
- Practice an oral rinse after brushing your teeth to get rid of germs.
- Reduce the consumption of acidic foods: lemons, tomatoes, kiwis, pineapples, etc.
- Avoid excess of spicy and spicy foods.

Some natural remedies can also be useful for calming discomfort. For example, specialist Raúl C. Peña explains that propolis extract exerts an antibiotic action.
In addition to this, an article published in the Journal of the Indian Society of Periodontology reports the benefits of the anti-inflammatory, healing and antimicrobial properties of calendula.
Pharmacological treatment of aphthous stomatitis
The treatments generally prescribed by the doctor in case of aphthous stomatitis are:
- Cyanoacrylate-based ointments, to be applied on the lesion. They act as a glue and avoid contact of food and saliva with the lesion.
- Topical anesthetics, such as lidocaine or benzocaine, which relieve pain.
- Topical corticosteroids for the realization of rinses or for application in the form of ointment based on fluocinonide, clobetasol or dexamethasone.
- For major lesions, it is possible to have steroid injections into the ulcer or have a CO2 laser treatment.
- Increase the consumption of foods containing folic acid, B vitamins and iron, as well as apples, yogurt, bananas, mangoes, legumes, etc.
- Gargling with antiseptic water and salt and / or hydrogen peroxide. Both help calm the symptoms.
If rapid improvement is not achieved or if the episodes recur several times a year, seek medical attention. He will make a correct diagnosis and rule out the presence of other more serious diseases.