Hyperhidrosis: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment

Hyperhidrosis is a condition where the human body sweats abnormally. It is excessive sweating not caused by a specific event or situation in particular.
It is natural to expect increased sweating on extremely hot days or during physical activity. In the case of hyperhidrosis, however, excessive sweating is not triggered by these situations, but is constant.
Sweat is made up of water: only 1% is made up of salts. The body produces it in the sweat glands to regulate body temperature. It is the nervous system that orders the body to sweat more or less depending on the situation.
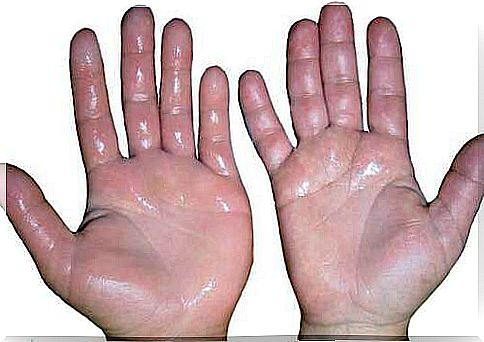
Although it affects all of the skin, sweating is most noticeable in the hands, feet and armpits. When moisture is stored for too long, the skin can become irritated and give off bad odors due to the breakdown of sweat by bacteria. In this case we speak of bromhidrosis.
It is estimated that 2% of the world population suffers from hyperhidrosis. It is common for this disorder to be familial, which is why parents and children, or siblings, have the same problem.
Causes of hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis can be attributed to two general causes: primary, or idiopathic, and secondary. The most common form is primary hyperhidrosis, which is self-producing.
The primary type is called focal essential hyperhidrosis. The problem affects the nerves that innervate the glands, which are more active than normal, which is why they continually stimulate the production of sweat. Although sweat is not associated with heat or exercise, it can increase with stress.
On the other hand, the secondary causes of hyperhidrosis are varied. These are diseases that have increased sweating among their symptoms. Among these we have:
- Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism : Thyroid hormones, as metabolic regulators, can influence the production of sweat.
- Diabetes : In some people, excessive sweating of the trunk raises suspicions about the possibility of suffering from diabetes.
- Coronary ischemic disease : In acute cardiac episodes, excessive sweating can be caused by the stimulus that pain generates on the sympathetic nervous system.
- Infections : Partly due to fever and partly due to accelerated metabolism during infection, the acute phase is usually accompanied by hyperhidrosis.
- Neuropathies : specifically, diseases of the peripheral nerves and the sympathetic nervous system alter the structure of the sweat glands.

Diagnostic criteria and symptoms
Excess sweating cannot always be traced back to a condition of hyperhidrosis. The medical community, in fact, has established some diagnostic criteria.
The first condition is to suffer for more than six months of profuse sweat without a direct explanation. In other words, when sweat appears even if it is not hot or in the absence of strenuous exercise. In addition to this criterion, at least two of the following circumstances must arise:
- It affects daily activities.
- Appearance of excessive sweating at least once a week.
- Suffering from it before the age of twenty-five.
- Having a family member with diagnosed hyperhidrosis.
- Sweat symmetrically: under both armpits, for example, at the same time.
- Sweating at night in winter.
Treatments for hyperhidrosis
- Antiperspirants : the first measure to be taken to combat hyperhidrosis. Usually the person decides to use an antiperspirant even before consulting the doctor. It seems that the most effective ingredient is aluminum chloride. However, it is easy to suffer from skin irritation, especially if you have sensitive skin.
- Medications : Although there are medications to reduce sweating, they are not always indicated due to their side effects.
- Iontophoresis : this technique uses electricity to destroy the action of the sweat glands. It involves a series of sessions and has so far shown no side effects. The current flow is constantly monitored and never reaches dangerous levels for the organism.
- Botulinum toxin : this substance is injected directly into the area most affected by hyperhidrosis to block the nerves that cause sweating. It can be injected in the armpits, hands and feet.
- Surgical intervention : the surgical procedure par excellence against hyperhidrosis is endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy. It is reserved for cases of maximum severity, for which the quality of life is compromised or skin infections are very frequent. It consists of cutting a nerve in the sympathetic nervous system to stop the stimulation of the sweat glands.