Pulmonary Edema: Symptoms And Causes
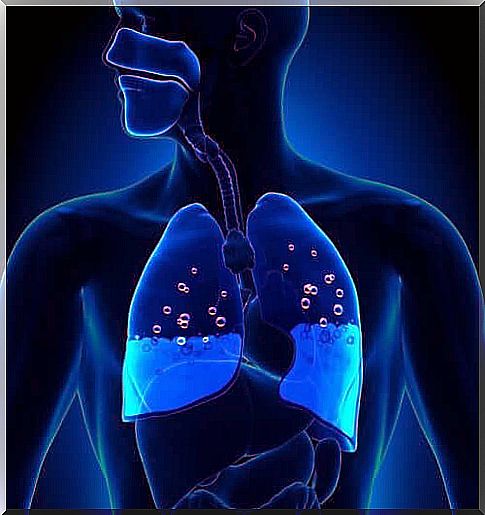
Pulmonary edema is a disease that consists of the accumulation of fluid in the lungs. This accumulation makes breathing difficult and, for this reason, puts the patient’s life at risk.
In most cases, pulmonary edema originates from a heart problem. However, it can also be caused by trauma, pneumonia (lung infection), or even medication.
When edema appears suddenly, it becomes a medical emergency, as it can be fatal. In other cases, it occurs gradually. But even so it is a serious condition, which we must try to solve.
In this article we explain what pulmonary edema consists of, what are its causes and its symptoms.
What does pulmonary edema consist of?
The alveoli are bags of air that together form the lungs. They have the task of absorbing oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide during breathing. When they are filled with liquid instead of air, this gas exchange cannot take place properly.
The accumulation of fluid is called pulmonary edema. It usually occurs due to heart problems and in this case it is called cardiogenic pulmonary edema. It mainly occurs when the left ventricle of the heart weakens.
However, pulmonary edema may not be associated with the heart (non-cardiogenic edema). This happens, for example, when a person climbs high altitude areas.
What are the causes of pulmonary edema?
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
As we have already mentioned, cardiogenic pulmonary edema occurs due to heart disease. Heart disorders that trigger pulmonary edema are usually:
- Anomalies of the coronary arteries. They are those in charge of the circulation of the heart. They tend to become clogged usually due to accumulation of fat (plaques of atheroma), which causes a weakening of the heart. Blood tends to accumulate in the lungs and this causes fluid to pass to the alveoli.
- Injuries of the heart muscle. Also called cardiomyopathy. What was described in the previous case occurs. Since the heart does not beat strongly enough, the fluid flows back to the lungs.
- Heart valve problems.
- Hypertension.
Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema
In this case, the main causes are:
- High altitudes. When a person climbs significant heights, an increase in pressure can occur due to the vascular constriction of the pulmonary capillaries. This causes the liquid to pass to the alveoli.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome. This is a condition where the lungs fill with fluid and white blood cells. It can be due to trauma or infection.
- Medicines.
- For pulmonary embolism. It occurs when a clot occupies a lung blood vessel and prevents blood from circulating regularly.
- Viral infections.
- Inhalation of smoke or suffocation.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms depend on the cause and how quickly edema forms. When it occurs in acute form, the main symptoms are:
- Breathing difficulty, worsening if the patient lies down.
- Feeling of asphyxiation.
- Noises when breathing (dyspnoea).
- Cough accompanied by possible blood stains.
- Tachycardia, with the heart beating at a rapid rate.
- The skin can become very cold and clammy, and the lips blue.
When edema appears gradually, the symptoms are slightly different:
- Also in this case there is a difficulty in breathing, both during the effort phase and when you lie down.
- The legs tend to swell.
- Increases the feeling of fatigue.
- The cough appears as soon as you lie down and calms down when you get up to sit down.
- Weight gain.
How can we prevent the problem?
To try to prevent pulmonary edema, the main precaution is to prevent heart disease. IS blood pressure must be kept under control, as hypertension is one of the main risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Getting moderate exercise every day and eating a balanced diet are essential measures. They help keep blood pressure levels and blood cholesterol under control. This is important because cholesterol is associated with coronary artery disease.
On the other hand, you should avoid smoking and drinking alcohol and it is advisable to maintain a healthy weight. Finally, of course, you have to try to keep stress under control.
To conclude
If you experience breathing difficulties, fatigue or any of the symptoms we have discussed, do not hesitate to seek urgent medical attention. Pulmonary edema is a delicate, health-threatening condition.